Types of Flooring Technology
The performance of a floor depends on the design, specification and the techniques used in its construction.
1.Large Area Pour – Laser Screed – Jointed / Saw Cut Floor
2.Large Area Pour – Laser Screed – Jointless
Large Pour- Laser Screed Flooring

State of the art laser screed technology from Somero USA is deployed at site (S-15R, with a telescopic boom of 6.1m M and with a 3 M head consisting of augur) laying 900 -1500 M2 per day. Imported flattening tools like professional (magnesium) key hole bump cutters, highway straightedge, power floaters and ride on trowels. Adjustable wooden shuttering with L-angle is used to handle a slump of 130mm (Slump window of ± 20 MM)
Large Area Pour – Laser Screed – Jointless floor (625 to 1225 M2 Pour)
Floor constructed in large panels without intermediate joints. This is constructed in the same manner as the jointed floor described above, but no joints are sawn. Jointless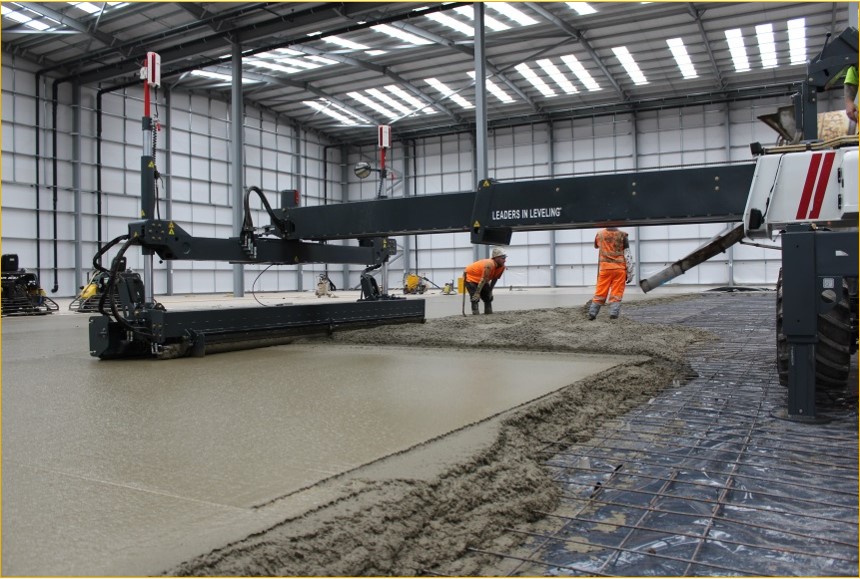 floors require good control of sub-base flatness and levelness to reduce the restraint on the underside of the slab. Often 35kg/m3 of steel fibre is used to control the distribution and width of the cracks caused by drying shrinkage stresses. The large distances between construction joints can often result in wider openings. Careful consideration should be given to the location of these joints and the impact they have on trucks. Hence all construction joints are replaced with Steel Armoured Joints at the edges of each panel.
floors require good control of sub-base flatness and levelness to reduce the restraint on the underside of the slab. Often 35kg/m3 of steel fibre is used to control the distribution and width of the cracks caused by drying shrinkage stresses. The large distances between construction joints can often result in wider openings. Careful consideration should be given to the location of these joints and the impact they have on trucks. Hence all construction joints are replaced with Steel Armoured Joints at the edges of each panel.
Long strip construction/ VNA Floors
The floor is laid in a series of strips typically 4 to 6m wide, with forms along each side. Strips can be laid alternately, with infill strips subsequently placed. Strips are laid in a continuous operation and joints are sawn transversely across each strip up to 6m apart to accommodate longitudinal shrinkage.
As formwork can be set to tight tolerances and as the distance between the forms is relatively small, this method lends itself to the construction of floors with a high standard of surface regularity such as VNA.
For VNA applications a DM Specification should be used and the category defined by the racking height. A high standard of floor flatness is an essential requirement for safe and efficient operation of a narrow aisle forklift truck. The static lean table (below) indicates how the potential for truck lean is increased by lifting height.
iNDUS+ ’No Joint’ Solution
iNDUS+ ’No Joint’ Solution is a totally seamless floor slab without any opening joints across the whole floor slab area, whatsoever no matter how large the surface of your floor.
The floor slab design combines high performance and high impact resistance Special double hook end steel fibres with steel mesh / rebar which ensures the surface of Combi - Slab floor remains intact even with intensive usage.
Also the Top steel reinforcement is continuous across the day end joints ‘Construction Joints’ which are converted to Tied Joints. The use of top mesh within the slab offers significantly improved crack control allowing a maximum crack opening within the floor slab to be guaranteed.
Suitable for ground bearing slabs for following applications:-
VNA Floors
Deep Freeze (- 250 C) stores
Mobile pallet racking
Advantages
Further reduced life cycle cost as slab resulting in higher business operational efficiencies and reduced maintenance.
No opening joints or saw cuts means that no joint sealing is required. A totally seamless floor slab will reduce ongoing maintenance to MHE equipment as not trafficking over any joints.
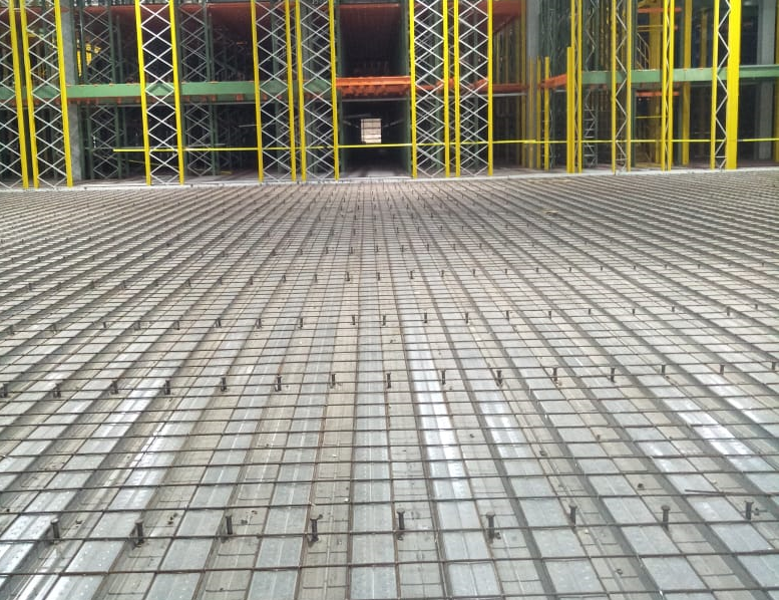
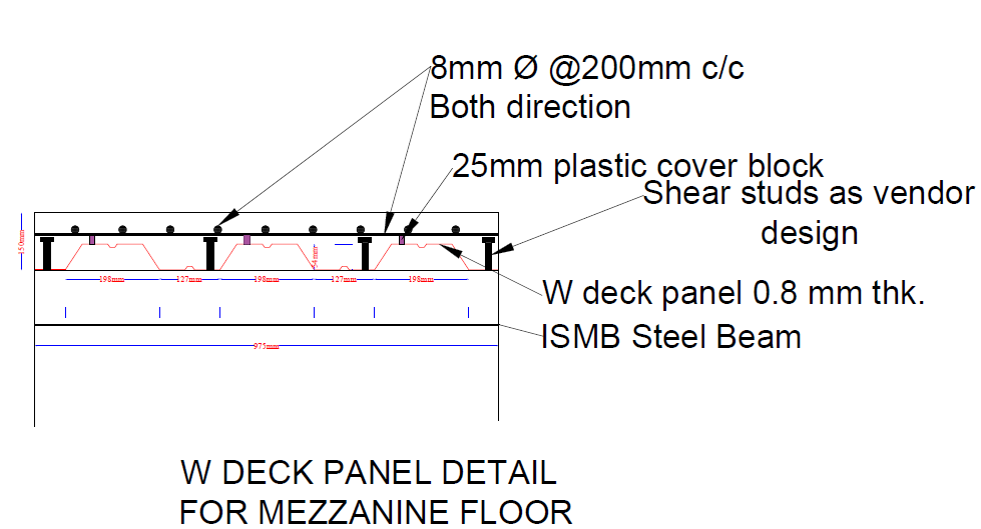
Mezzanine Composite Deck Slab with Studs -150 mm Thk.
Typical Specification for Mezzanine Deck Slabs:- Deformed Steel Bar Reinforcement: Supplying, Laying, Cutting Fixing in position Steel bar (8 mm Diameter bar @ 200 mm c/c spacing in both directions at Top level) and locations as shown in Mezzanine deck floor structural drawing. Steel Reinforcement / Mesh should be placed with 25 mm plastic cover blocks and with proper overlap in both the directions. Overall Deck Slab Depth – 150 MM
 |
 |

 0124-4042124
0124-4042124
